Introduction
EGR Cooler, Enhance engine health, boost fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions with exhaust cooling. Discover top tips to tackle common issues. This cooler, a part of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, is often overlooked, yet it significantly impacts the performance and longevity of car engines.
For those who own diesel or gasoline vehicles, understanding this cooler can help maintain engine health, optimize fuel economy, and reduce environmental impact. This article will explore everything you need to know about this cooler, from its functions to common issues and maintenance tips.
Table of Contents
What is an EGR Cooler?
The EGR cooler, short for Exhaust Gas Recirculation cooler, is a vital component of a vehicle’s emission control system. It serves to cool down the exhaust gases before they re-enter the engine’s intake manifold, which plays an important part in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. By lowering the temperature of these gases, this cooler helps minimize the production of pollutants, which is essential for meeting environmental standards.
Understanding the EGR System
To appreciate the function of the EGR cooler, it’s helpful to first understand the broader EGR system. The Exhaust Gas Recirculation system works by redirecting a portion of an engine’s exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber. This dilution process reduces the temperature within the combustion chamber, which, in turn, lowers the amount of nitrogen oxides (NOx) produced—a significant contributor to air pollution.
The Purpose of the EGR Cooler
The EGR cooler’s main job is to lower the temperature of the recirculated exhaust gases before they enter the engine. Cooler gases mean a cooler combustion process and cooler combustion processes result in fewer nitrogen oxides being generated. Since NOx is a harmful emission that is heavily regulated, having a functioning cooler is essential for compliance with emission standards, especially in diesel engines where NOx formation is more pronounced.
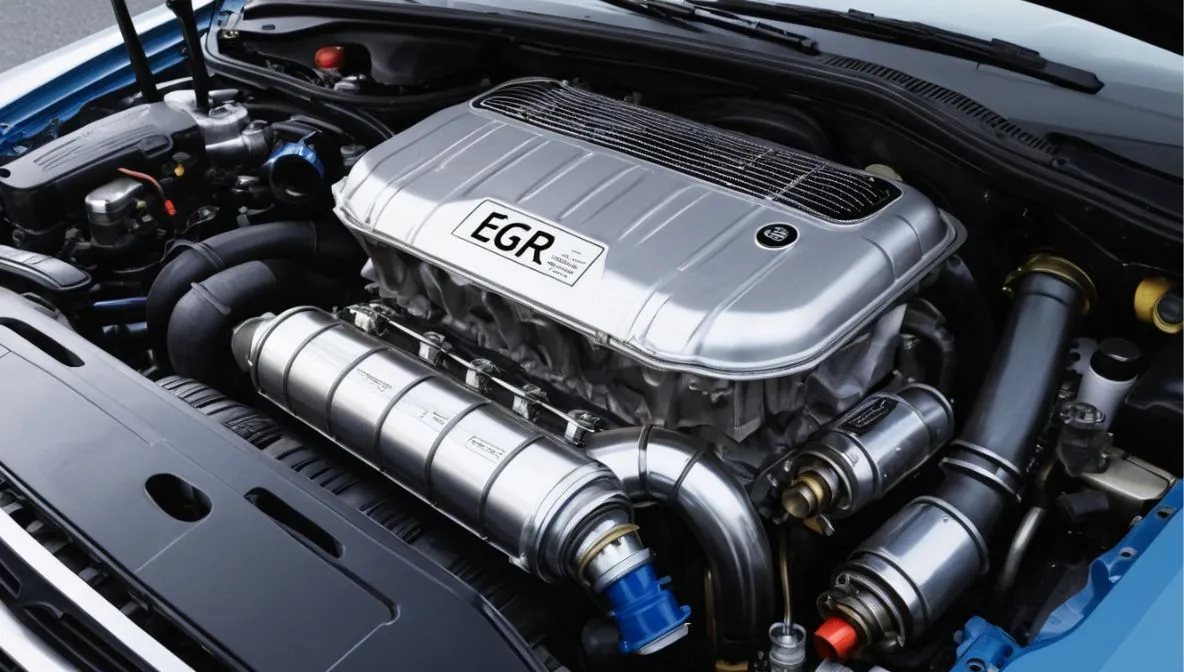

Why is the EGR Cooler Important?
The importance of the EGR cooler extends beyond emissions control. Its impact on engine performance and fuel efficiency makes it a valuable component in modern engines. Here’s why maintaining this cooler is essential for your car’s overall health:
Reducing Emissions and Meeting Environmental Standards
The primary purpose of the EGR cooler is to aid in reducing harmful emissions, particularly NOx. When exhaust gases are cooled before being reintroduced into the engine, the result is a cleaner burn, lowering the vehicle’s NOx output. In areas where emissions regulations are stringent, such as California or the European Union, a properly functioning EGR cooler is critical for meeting legal requirements.
Contributing to Engine Health
A secondary benefit of the EGR cooler is its role in maintaining engine temperature balance. By cooling the recirculated exhaust gases, it prevents the engine from overheating, which could lead to serious damage. An overheated engine can cause premature wear on engine components, leading to costly repairs down the line. Thus, this cooler indirectly helps extend the life of your vehicle’s engine.
Improving Fuel Efficiency
In addition to emissions and engine health, an EGR cooler can positively impact fuel efficiency. Engines that operate at cooler temperatures are generally more efficient, as fuel combustion happens more effectively in a controlled, cooler environment. For drivers, this means potentially lower fuel costs over time, especially if driving long distances is a regular part of their routine.

How Does an EGR Cooler Work?
Understanding how an EGR cooler functions within the engine can shed light on why it’s such an important component.
Toyota, for example, emphasizes advanced emissions technologies in their vehicles, highlighting the importance of effective emissions systems.
Ford’s EGR systems in their diesel models (like the 6.0 Powerstroke) highlight the role of EGR coolers in maintaining low emissions and high efficiency.
Let’s walk through each stage of this cooler’s operation in detail:
Step 1: Redirection of Exhaust Gases
The process begins when the EGR system diverts a portion of the exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold. Instead of allowing all exhaust gases to exit through the tailpipe, the EGR system routes a controlled amount back into the engine’s intake manifold. At this point, the EGR cooler takes on its crucial role.
Step 2: Cooling the Exhaust Gases
The extremely hot exhaust gases pass through this cooler. Inside the cooler, the gases flow through a network of tubes that allow heat to dissipate. Typically, this cooler uses coolant or air to absorb the heat from these exhaust gases. As the gases pass through the cooler, their temperature drops significantly, making them less likely to contribute to high combustion temperatures when they are reintroduced into the engine.
Step 3: Reintroducing Cooled Gases into the Engine
Once the exhaust gases have been cooled, they are directed back into the engine’s intake manifold, where they mix with fresh air and fuel. This cooled mixture then undergoes combustion. The lower combustion temperature leads to a reduction in NOx emissions, allowing the vehicle to run cleaner and more efficiently.
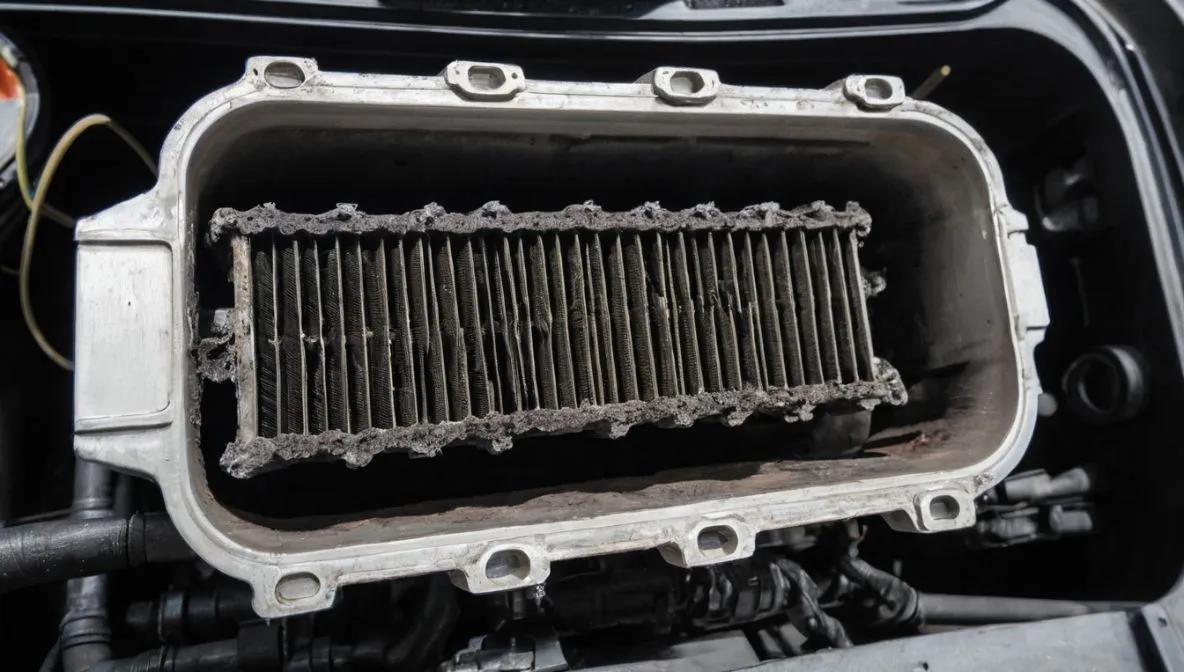
Common EGR Cooler Problems and How to Diagnose Them
Like any automotive component, the EGR cooler can encounter issues over time, especially if it’s not maintained properly. Common problems with these coolers include clogging, leaks, and general wear and tear. Be mindful of these potential issues:
Clogging of the EGR Cooler
One of the most frequent issues with EGR coolers is clogging. Over time, carbon deposits from the exhaust gases can build up inside the cooler, reducing its efficiency. When a cooler becomes clogged, it can’t cool the gases as effectively, leading to higher temperatures in the combustion chamber and increased NOx emissions. This not only affects emissions compliance but can also lead to engine overheating.
Leaks in the EGR Cooler
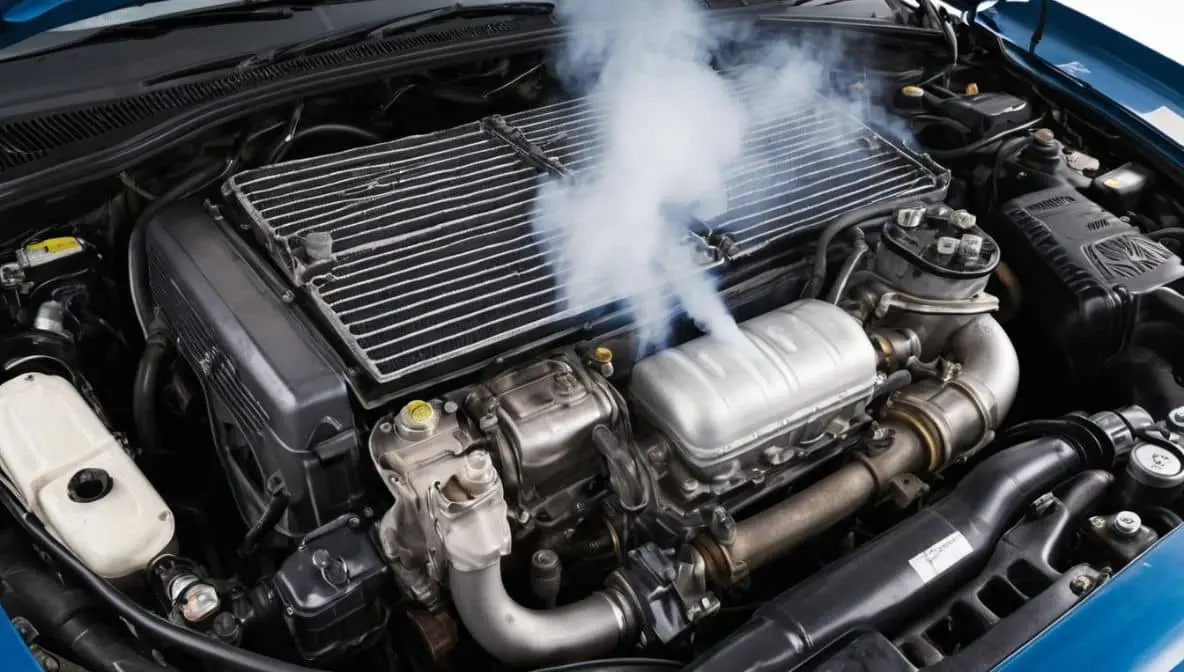
EGR coolers can develop leaks, often due to cracks or corrosion within the unit. When leaks occur, coolant can escape from the cooler, reducing the vehicle’s overall coolant levels and potentially leading to overheating. In severe cases, coolant may mix with the exhaust gases, which can cause white smoke to emanate from the exhaust. If you notice a drop in coolant levels or visible white smoke, it may be a sign of a leaking cooler.
Symptoms of a Faulty EGR Cooler
Identifying a faulty EGR cooler early on can help prevent more extensive damage to the engine. Key indicators of a malfunctioning cooler often include the following:
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: If the cooler isn’t functioning properly, fuel consumption may increase.
- Engine Overheating: A faulty cooler can lead to higher engine temperatures, causing the engine to overheat.
- Increased Emissions: Higher levels of NOx emissions may be noticeable, especially during emissions testing.
If you encounter any of these symptoms, a professional must check the EGR cooler to avoid further issues.

Tips for Maintaining an EGR Cooler
Proper maintenance of the EGR cooler can extend its lifespan and improve vehicle performance. Here are a few essential tips:
Regular Cleaning to Prevent Clogs
To avoid clogging, schedule regular EGR system cleanings. During these cleanings, a mechanic can remove carbon deposits from the cooler and other parts of the EGR system, restoring its efficiency. Many vehicle owners overlook this step, but regular cleaning can significantly improve the cooler’s function and prevent costly repairs down the line.
Monitor Coolant Levels
Since the EGR cooler often relies on coolant, it’s essential to keep an eye on coolant levels. If you notice a sudden drop, it could indicate a leak within this cooler. Addressing this early can prevent overheating and further damage to the engine.
Seek Professional Service When Necessary
While some maintenance tasks can be handled independently, certain issues, like leaks or extensive clogging, require professional service. A mechanic can assess the condition of the EGR cooler and perform any repairs or replacements needed to keep it in optimal working condition.

FAQs About EGR Coolers
The EGR cooler can be a complex component to understand, especially for those new to car maintenance. Below are answers to some frequently asked questions that can help clarify its purpose, maintenance, and potential issues.
How often should an EGR cooler be cleaned?
Cleaning frequency for an EGR cooler depends on factors like vehicle type, driving habits, and the quality of fuel used. Generally, it’s recommended to clean this cooler every 50,000 miles or as part of regular EGR system maintenance. Diesel engines may require more frequent cleaning due to the higher likelihood of carbon buildup. Regular cleaning helps keep the cooler functioning efficiently, preventing issues like clogging, which can lead to overheating and higher emissions.
In some cases, car owners may notice a drop in fuel efficiency or rough idling, which could indicate that this cooler is due for a cleaning. By including this cooler in routine maintenance, car owners can prevent larger, costlier issues and ensure the EGR system performs optimally.
Can I drive with a faulty EGR cooler?
Technically, a car can still be driven with a malfunctioning EGR cooler, but it’s not advisable. A faulty cooler can lead to increased NOx emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential engine overheating. Prolonged driving under these conditions may cause further engine damage, which can lead to costly repairs or even permanent damage to the engine.
Driving with a malfunctioning cooler also increases your environmental footprint. Emissions may exceed legal limits, which could lead to issues during vehicle inspections or emissions testing. If you suspect your cooler isn’t working correctly, it’s best to have it inspected and repaired by a professional as soon as possible.
How much does it cost to replace an EGR cooler?
The cost of replacing an EGR cooler can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle, as well as labor rates in your area. On average, this cooler replacement costs can range from $300 to $1,000, with parts and labor included. For high-end or luxury vehicles, the cost may be even higher due to specialized parts or labor requirements.
While it may seem costly, a functioning EGR cooler is essential for vehicle performance and emission compliance. Investing in timely replacement or repair can prevent more severe engine issues, saving car owners from even higher expenses down the road.
What are the signs of a leaking EGR cooler?
A leaking EGR cooler typically presents symptoms such as a noticeable drop in coolant levels, white smoke from the exhaust, or engine overheating. Leaks often develop due to wear and tear over time or exposure to extreme engine conditions. When leaks occur, coolant may escape from the cooler, leading to decreased cooling system efficiency.
If coolant mixes with exhaust gases, it can cause white smoke to emanate from the exhaust—a telltale sign of a leak. Leaks can also result in low coolant levels, which may trigger the engine to overheat. Addressing a leaking cooler promptly is essential for maintaining optimal engine function and preventing more serious issues that could require extensive repairs.
Is EGR cooler maintenance necessary for all vehicles?
While not all vehicles are equipped with EGR coolers, they are common in diesel and certain gasoline engines designed to meet strict emission standards. If your vehicle has a cooler, maintenance is essential to ensure it functions correctly and continues to reduce harmful emissions. For vehicles without this cooler, general maintenance of the EGR system is still beneficial for emission control and engine efficiency.
Recently, EGR coolers have become more common in vehicles designed to meet stringent emissions standards. If your car has this cooler, regular maintenance will be critical for keeping the component in good condition. Vehicles without this cooler should still receive EGR system maintenance, as keeping emissions under control benefits both performance and regulatory compliance.

Tips for Extending the Life of Your EGR Cooler
Proper maintenance practices can prolong the life of your EGR cooler, keeping your engine running smoothly and minimizing emission levels. Explore these useful tips to maximize the efficiency of your cooler.
Use High-Quality Fuel
Poor-quality fuel often leads to increased soot and carbon buildup within the EGR cooler and other components of the EGR system. Opting for high-quality fuel reduces the likelihood of clogging and enhances the overall efficiency of your vehicle’s emissions control. While quality fuel may cost more upfront, it can save you from frequent maintenance and repairs in the long run.
Soot buildup in this cooler is a common issue that can cause the cooler to lose its effectiveness over time. By investing in high-quality fuel, you help prevent excessive deposits, which keeps this cooler operating smoothly and reduces the need for frequent cleaning.
Perform Regular Engine Maintenance
Routine maintenance, including regular oil changes, air filter replacements, and periodic inspections, helps keep the EGR cooler and the entire EGR system in good condition. When engine components are well-maintained, the likelihood of contaminants affecting this cooler decreases, contributing to a longer component lifespan.
In addition to oil changes and air filter replacements, it’s a good idea to schedule EGR system check-ups as part of your routine maintenance. During these check-ups, a technician can examine this cooler for any signs of wear or damage and address issues early on before they affect engine performance.
Avoid Prolonged Idling
Prolonged idling leads to a buildup of soot within the EGR system, as the engine runs inefficiently at low speeds. Whenever possible, avoid leaving your vehicle idling for extended periods, as it can accelerate carbon accumulation in this cooler. Limiting idling time is particularly important for diesel vehicles, which tend to produce more soot at low speeds.
Frequent idling also increases fuel consumption and can cause other components, like the exhaust system, to accumulate carbon deposits. Reducing idling time contributes to better fuel efficiency and less strain on the EGR cooler, ensuring it lasts longer.
Address Issues Promptly
If you notice any symptoms of EGR cooler failure, such as decreased fuel efficiency or increased emissions, don’t delay in seeking professional help. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from turning into costly repairs, saving you time and money. By addressing these cooler problems as soon as they arise, you can maintain your vehicle’s performance and ensure compliance with emissions standards.
In some cases, a simple cleaning can resolve early signs of clogging or other minor issues. However, if left unaddressed, small issues can quickly escalate. Proactive maintenance can make a significant difference in the lifespan of your EGR cooler and contribute to overall engine health.
Conclusion
The EGR cooler is an essential component in modern car engines, designed to reduce harmful emissions and maintain efficient engine performance. By cooling exhaust gases before they re-enter the engine, this cooler contributes to lower NOx emissions, improved fuel economy, and a balanced combustion process. Understanding how this component works, recognizing the signs of failure, and implementing regular maintenance practices can go a long way in extending the life of this cooler and, by extension, the vehicle’s engine.
Maintaining this cooler not only meets environmental standards but also helps avoid costly repairs down the road. With preventative maintenance like regular cleaning, monitoring coolant levels, and using quality fuel, you can keep your cooler in peak condition, ensuring that your vehicle runs smoothly and cleanly for years to come. Ultimately, this cooler’s impact on both performance and emissions highlights its importance in modern vehicles, making it a component worth understanding and caring for.
To further enhance your vehicle’s performance, don’t miss our article on ‘6.0 Powerstroke: Discover Incredible Performance, Fix Issues, and Upgrade Now.‘ Dive in to uncover tips that will elevate your driving experience!

